Libraries Available
The following table summarizes the gene-modulation libraries available. For more detailed information, follow the links or scroll down the page. Frequently asked questions about these libraries can be found here.
TRC Libraries
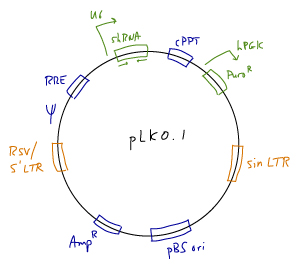 The TRC Genome-Wide shRNA Collections for human and mouse were developed by The RNA Consortium.
The TRC Genome-Wide shRNA Collections for human and mouse were developed by The RNA Consortium.
- shRNA design: Simple hairpin
- Vector: pLKO.1 lentiviral vector. A full vector map and sequence are available in this document from the Broad Institute's Public TRC Portal.
- Promoter: U6 (Pol III promoter)
- Marker: None
- Antibiotic resistance: Puromycin
- Human library coverage:
- Approximately 15,000 genes
- Average of about 5 shRNAs per gene
- Mouse library coverage:
- Approximately 15,000 genes
- Average of about 5 shRNAs per gene
- Rat coverage (due to homology to human and mouse):
- Over 10,000 genes
- Average of about 2 shRNAs per gene
- Clones are stored in the library as bacterial cultures of E. coli DH5α.
References:
- Root DE, Hacohen N, Hahn WC, Lander ES, Sabatini DM. (2006) Genome-scale loss-of-function screening with a lentiviral RNAi library. Nature Methods 3:715.
- Moffat J, Grueneberg DA, Yang X, Kim SY, Kloepfer AM, Hinkle G, Piqani B, Eisenhaure TM, Luo B, Grenier JK, Carpenter AE, Foo SY, Stewart SA, Stockwell BR, Hacohen N, Hahn WC, Lander ES, Sabatini DM, Root DE. (2006) A lentiviral RNAi library for human and mouse genes applied to an arrayed viral high-content screen. Cell 124:1283.
GIPZ Libraries
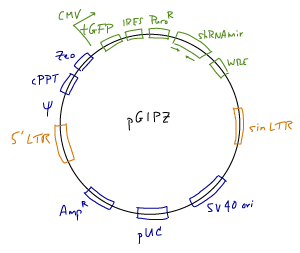 The GIPZ Lentiviral shRNAmir Libraries were developed by Open Biosystems (Thermo Scientific) in collaboration with Greg Hannon (CSHL) and Steve Elledge (Harvard).
The GIPZ Lentiviral shRNAmir Libraries were developed by Open Biosystems (Thermo Scientific) in collaboration with Greg Hannon (CSHL) and Steve Elledge (Harvard).
- shRNA design: shRNAmir. The shRNA hairpin is placed in the context of the mir-30 sequence.
- Vector: pGIPZ lentiviral vector. Details are available at the Open Biosystems website; a vector map and sequence are available here.
- Promoter: CMV (Pol II promoter)
- Marker: GFP
- Antibiotic resistance: Puromycin
- Human library coverage:
- Approximately 18,000 genes
- Average of about 5 shRNAs per gene
- Mouse library coverage:
- Over 16,000 genes
- Average of 3-4 shRNAs per gene
- Rat coverage (due to homology to human and mouse):
- Over 10,000 genes
- Average of about 2 shRNAs per gene
- Clones are stored in the library as bacterial cultures of E. coli PrimePlus a version of JM109 modified for increased stability.
Reference:
- Silva JM, Li MZ, Chang K, Ge W, Golding MC, Rickles RJ, Siolas D, Hu G, Paddison PJ, Schlabach MR, Sheth N, Bradshaw J, Burchard J, Kulkarni A, Cavet G, Sachidanandam R, McCombie WR, Cleary MA, Elledge SJ, Hannon GJ. (2005) Second-generation shRNA libraries covering the mouse and human genomes. Nature Genetics 11:1281.
Decode Pooled shRNA Library
The Decode RNAi-GIPZ Whole Genome Pooled Screening Library from Open Biosystems (Thermo Scientific) is designed for use in selection-based screening, with hit identification by next-generation sequencing of the hairpin region.
- shRNA design: shRNAmir. The shRNA hairpin is placed in the context of the mir-30 sequence.
- Vector: pGIPZ lentiviral vector. Details are available at the Open Biosystems website; a vector map and sequence are available here.
- Promoter: CMV (Pol II promoter)
- Marker: GFP
- Antibiotic resistance: Puromycin
- Human pooled library coverage:
- Approximately 50,000 clones targeting human genes, spread across 7 separate pools. Each pool targets approximately 6,000 genes, with some overlap between pools. The entire set targets over 20,000 genes, with each targeted by 2-3 shRNAs on average.
Reference:
- Strezoska Z, Licon A, Haimes J, Spayd KJ, Patel KM, Sullivan K, Jastrzebski K, Simpson KJ, Leake D, van Brabant Smith A, Vermeulen A. (2012) Optimized PCR conditions and increased shRNA fold representation improve reproducibility of pooled shRNA screens. PLoS ONE 7:e42341.
DECIPHER Pooled shRNA Library
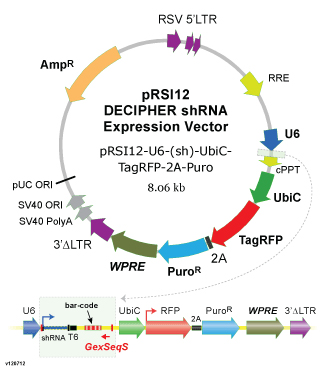 The DECIPHER Pooled Lentiviral shRNA Libraries from Cellecta is designed for use in selection-based screening, with hit identification by next-generation sequencing of a unique barcode sequence incorporated into each clone.
The DECIPHER Pooled Lentiviral shRNA Libraries from Cellecta is designed for use in selection-based screening, with hit identification by next-generation sequencing of a unique barcode sequence incorporated into each clone.
- shRNA design: Simple hairpin
- Vector: pRSI12 lentiviral vector. See details here.
- Promoter: U6 (Pol III promoter)
- Marker: RFP
- Antiobiotic resistance: Puromycin
- Human pooled library coverage:
- Module 1 (~5,000 targets, 27,500 shRNAs)
- Module 2 (~5,400 targets, 27,500 shRNAs)
- Module 3 (~5,000 targets, 27,500 shRNAs)
- Mouse pooled library coverage:
- Module 1 (~5,000 targets, 27,500 shRNAs)
- Module 2 (~5,000 targets, 27,500 shRNAs)
CRISPR Pooled Libraries
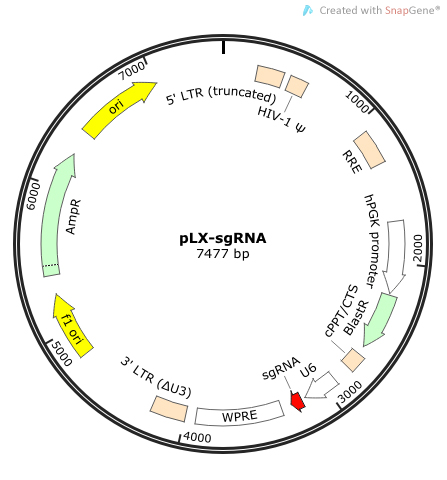 The Human Lentiviral sgRNA Libraries, developed by the David Sabatini and Eric Lander labs (MIT/Broad Institute), are designed for use in selection-based screening, with hit identification by next-generation sequencing of the sgRNA.
The Human Lentiviral sgRNA Libraries, developed by the David Sabatini and Eric Lander labs (MIT/Broad Institute), are designed for use in selection-based screening, with hit identification by next-generation sequencing of the sgRNA.
- Vectors: 2-vector system — pCW-Cas9, expressing Cas9 from an inducible promoter, snd pLX-sgRNA, expressing the sgRNA constitutively.
- Promoters:
- Cas9: Tet-responsive promoter with minimal CMV promoter (doxycycline-inducible Tet ON system)
- sgRNA: U6 promoter
- Marker: Cas9 tagged with FLAG; no marker on sgRNA vector
- Antibiotic resistance: Puromycin on Cas9 vector, blasticidin on sgRNA vector
- Design: 10 sgRNAs per gene
- Gene coverage:
- Kinase library: 507 genes
- Cell cycle library: 983 genes
- Nuclear protein library: 3,733 genes
Reference:
- Wang T, Wei JJ, Sabatini DM, Lander DS. (2014) Genetic screens in human cells using the CRISPR-Cas9 system.Science 343:80.
Precision LentiORF library
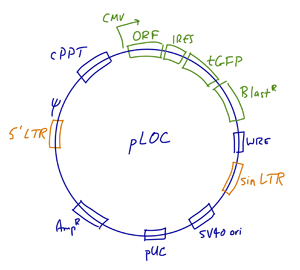 The Human Precision LentiORF Library from Open Biosystems (Thermo Scientific) is an expression-ready collection of open reading frames, generated using content from the sequence-validated ORFeome Collaboration collection.
The Human Precision LentiORF Library from Open Biosystems (Thermo Scientific) is an expression-ready collection of open reading frames, generated using content from the sequence-validated ORFeome Collaboration collection.
- Vector: pLOC lentiviral expression vector. Vector details are available here.
- We recommend sequencing all constructs for confirmation.
- Sequencing primers: Forward CTCCATAGAAGACACCGAC; Reverse CATATAGACAAACGCACAC.
- Promoter: CMV (Pol II promoter)
- Marker: GFP
- Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin
- Human library coverage: ~6,000 genes
hORFeome V8.1 Library
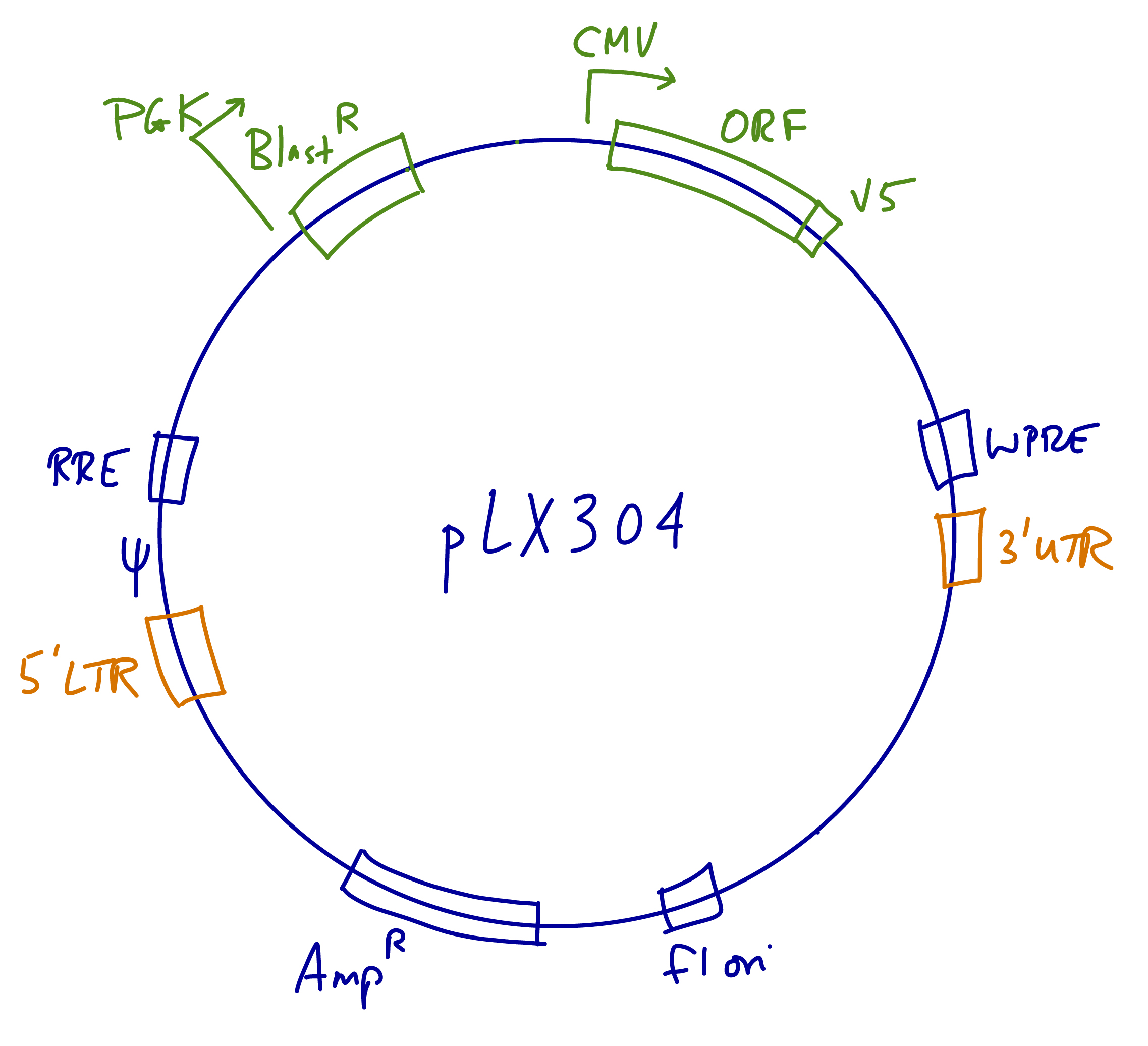 The hORFeome V8.1 Library was developed at the Broad Institute.
The hORFeome V8.1 Library was developed at the Broad Institute.
- Vector: pLX304 lentiviral expression vector. Vector details are available here.
- We recommend sequencing all constructs for confirmation.
- Sequencing primers: Forward (CMV-F) CGCAAATGGGCGGTAGGCGTG; Reverse (WPRE-R) CATAGCGTAAAAGGAGCAACA.
- Promoter: CMV (Pol II promoter)
- Marker: None. All ORFs are tagged with the V5 epitope.
- Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin
- Human library coverage: ~9,700 genes
Reference:
- Yang et al. (2010) A public genome-scale lentiviral expression library of human ORFs. Nature Methods 8:659.
Mammalian Genome Collection
The Mammalian Genome Collection was the result of a multi-institute effort based at the NIH, with the goal of producing at least one sequence-validated full-length clone for each known human and mouse gene.
- Vector: The clones in this collection are in a variety of vectors, some of which are mammalian expression vectors (but not lentiviral vectors). The most frequent vectors used are:
- pCMV-SPORT6. Sequencing primers: M13/pUC Forward (CCCAGTCACGACGTTGTAAAACG) and M13/pUC Reverse (AGCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGG).
- pCR4-TOPO. Sequencing primers: T3 (ATTAACCCTCACTAAAGGGA) and T7 (TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG).
- pOTB7. Sequencing primers: M13 (-21) Forward (TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGT) and M13 Reverse (CAGGAAACAGCTATGAC).
- pCR-BluntII-TOPO. Sequencing primers: M13 Reverse (CAGGAAACAGCTATGAC) and M13 (-21) Forward (TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGT).
- Many others are also represented in the collection.
- We recommend sequencing all constructs for confirmation.
- Human library coverage: ~17,000 genes
- Mouse library coverage: ~14,500 genes
Reference:
- Zuber et al. (2009) The completion of the Mammalian Genome Collection (MGC). Genome Research 19:2324.